Are you looking to learn more about biotin? Then you came to the right place!
Read on to learn 9 amazing fun facts about your favorite B-vitamin, biotin.
Known as vitamin B7, this nutrient is also often referred to as “vitamin H”. The “H” comes from the German words for hair and skin, “Haar und Haut.”
Biotin plays an important role in the body’s metabolism as a coenzyme. It helps to facilitate several enzymatic reactions, particularly those involved in the processing of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
Biotin acts as a carrier of carbon dioxide in the body, transferring it from one molecule to another as part of metabolic reactions. In this way, biotin helps to ensure the proper functioning of several metabolic pathways, including the citric acid cycle, which is crucial for producing energy in the form of ATP.
Additionally, biotin is involved in the synthesis of glucose from noncarbohydrate sources and in the production of fatty acids and cholesterol.
Overall, biotin plays a key role in maintaining the body’s metabolic balance and supporting its overall health.
Biotin is known to help support healthy skin, hair, and nails because of its role in the metabolism of fatty acids and in the production of keratin, the structural protein that makes up the hair, nails, and skin. A biotin deficiency can lead to brittle nails, hair loss, and skin rashes, while biotin supplementation has been shown to improve nail thickness and hair health.
When it comes to biotin, there’s no taking too much, since the body will just get rid of any biotin it isn’t going to be using right away.
The body also doesn’t store biotin, and the nutrient has a half-life of two hours within the body. This means that after two hours, the amount of biotin has been reduced by half, and in another two hours it will once again be reduced by half, then so on and so forth until it’s completely gone.
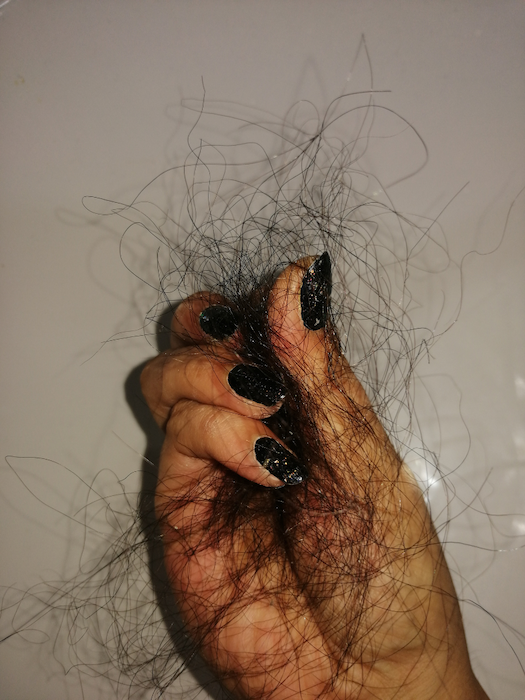
Biotin plays an important role in the health of skin, hair, and nails. As such, biotin deficiency can lead to skin rashes, hair loss, and brittle nails because biotin is involved in various metabolic processes, including the production of fatty acids, which are essential components of the skin and hair, and the metabolism of amino acids, which are the building blocks of nails.
Additionally, biotin is involved in the metabolism of glucose, which is essential for maintaining healthy skin. When there is a deficiency of biotin, these metabolic processes are disrupted, leading to symptoms such as skin rashes, hair loss, and brittle nails.
Gut bacteria have the ability to produce biotin. Biotin is synthesized by gut bacteria through the degradation of dietary proteins and the metabolism of certain amino acids. This process involves the production of biotin by gut bacteria, which is then absorbed through the intestinal wall and used to support various metabolic processes.
The amount of biotin produced by gut bacteria varies depending on the type and number of bacteria present, as well as on other factors such as diet, age, and health status.
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for biotin is as follows:
Remember, this is the bare minimum health agencies believe you should be getting in order to avoid a deficiency.

Biotin plays a role in promoting hair growth and preventing hair loss by supporting the health of hair follicles. Biotin does this by:
Regulating the metabolism of fatty acids: Biotin is involved in the metabolism of fatty acids, which are essential components of the hair follicle and hair shaft.
Supporting the production of keratin: Biotin helps in the production of the structural protein keratin, which makes up the hair shaft.
Improving blood circulation: Biotin helps improve blood circulation to the hair follicles, providing them with essential nutrients for growth.
Preventing oxidative stress: Biotin has antioxidant properties that protect the hair follicles from oxidative stress, which can damage hair growth.
Biotin is important for the health of several key body systems, including the eyes, liver, and nervous system.
Eye health: Biotin helps maintain healthy eyes by supporting the metabolism of fatty acids and glucose, which are important components of the retina and other parts of the eye.
Liver health: Biotin plays a role in liver function by assisting in the metabolism of amino acids and other nutrients, as well as in the production of glucose and the synthesis of fatty acids.
Nervous system: Biotin is involved in the production of energy and the metabolism of fats, amino acids, and glucose, which are all important for the proper functioning of the nervous system. Biotin also plays a role in the formation of certain neurotransmitters, which are chemical messengers that help transmit signals in the nervous system.
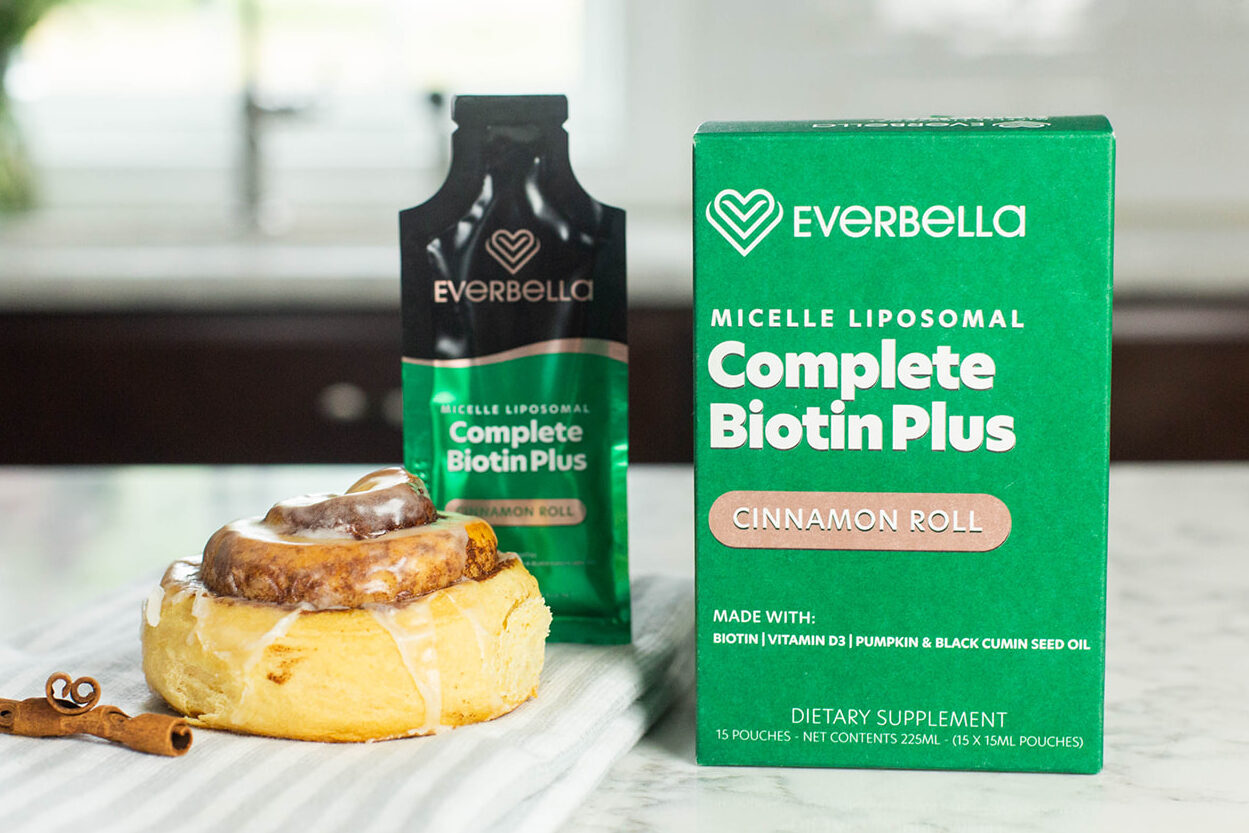
If you want your body to share in the fun of biotin, there’s no better way to get it than Complete Biotin Plus.
This is because EverBella’s formula contains a patented micelle liposomal formula which ensures proper absorption and use of the biotin.
But it also contains a few other incredible compounds that support beauty and health!